
AI Tutorial: Artificial Intelligence – An Introductory Guide
Artificial Intelligence means machines are designed and programmed in such a manner that they think and act like humans reducing human efforts. Nowadays, many industries or people are using this technology to develop machine learning devices to perform various activities. Using the machines to increase the speed of work and produce a quick and accurate result. Modern machines are generally capable of successfully understanding human speech, they also compete at the highest level in strategic game systems, autonomously operating cars, intelligent routing in content delivery networks, and military simulations.

Types of Artificial Intelligence
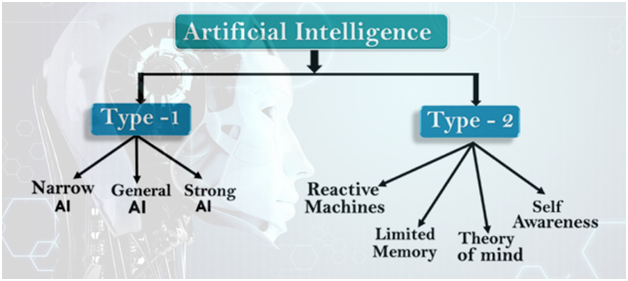
Type1: Based on Capabilities
Narrow AI
- Narrow AI is a type of AI that can perform a dedicated task with intelligence.
- The most common and presently available AI is Narrow AI in the world of Artificial Intelligence.
- Narrow AI cannot perform beyond its field or limitations, as it is only trained for a specific task.
- Apple Series is a good example of Narrow AI, but it operates with a limited pre-defined range of functions.
- IBM’s Watson supercomputer also comes under Narrow AI, as it uses an Expert system approach combined with Machine learning and natural language processing.
- Examples of Narrow AI are playing chess, purchasing suggestions on e-commerce sites, self-driving cars, speech recognition, and image recognition.
General AI
- General AI is a type of intelligence that can perform any task with efficiency like a human.
- The idea behind the general AI is to make a system that could be smarter and think like a human on its own.
- Nowadays, there is no such system exists which could come under general AI and can perform any task as perfectly as a human.
- Worldwide researchers are now focused on developing machines with General AI.
- Presently systems with general AI are still under research, and it will take lots of effort and time to develop such systems.
Super AI
- Super AI is a level of Intelligence of Systems at which machines could surpass human intelligence, and can perform any task better than a human with cognitive properties.
- Some characteristics of strong AI include capability including the ability to think, reason, solve the puzzle, make judgments, plan, learn, and communicate on its own.
- Super AI is a hypothetical concept of Artificial Intelligence.
- The development of such systems in real is still a world-changing task.
Type-2: Based on functionality
Reactive Machines
- Reactive machines are the common most basic types of Artificial Intelligence.
- Reactive machines do not store memories or past experiences for future actions.
- These machines mainly focus on current scenarios and react to them as per the possible best action.
- IBM’s Deep Blue system is an example of a reactive machine.
- Google’s Alpha Go is also an example of a reactive machine.
Limited Memory
- Limited memory machines can store previous experiences or some data for a short period.
- These machines can use stored data for a limited period only.
- Self-driving cars are one of the best examples of Limited Memory systems. These cars can store the recent speed of nearby cars, the distance of other cars, the speed limit, and other information to navigate the road.
Theory of Mind
- Theory of Mind means machines should understand human emotions, people, and beliefs, and be able to interact socially like humans.
- In present this type of AI machine is still not developed, but researchers are making lots of efforts and improvements to developing such AI machines.
Self-Awareness
- These machines will be super intelligent and will have their own decision, sentiments, and self-awareness.
- These machines will be smarter comparing the human mind.
- In present self-awareness, AI does not exist in reality still and it is a hypothetical concept.
Examples of AI technology
Automation
To make a system or process function automatically. For example, robotic process automation (RPA) can be programmed to perform high-volume, repeatable tasks that humans normally perform. Robotic process automation is different from IT automation in that it can adapt to changing circumstances.
Machine learning
It means the science of getting a computer to act without programming. Deep learning is a sublevel of machine learning that, in very simple terms, can be thought of as the automation of predictive analytics. There are three types of machine learning algorithms.
- Supervised learning
- Unsupervised learning
- Reinforcement learning
Machine vision
This technology captures and analyzes visual information using a camera, analog-to-digital conversion, and digital signal processing. It is often compared to human eyesight, but machine vision isn’t bound by biology and can be programmed to see through walls, for example. It is used in a range of applications from signature identification to medical image analysis. Computer vision, which is focused on machine-based image processing, is often conflated with machine vision.

Robotics
A field of engineering focused on the design and manufacturing of robots. Robots are often used to perform tasks that are difficult for humans to perform or perform consistently. They are used in assembly lines for car production or by NASA to move large objects in space. Researchers are also using machine learning to build robots that can interact in social settings.
Self-driving cars
These use a combination of computer vision, image recognition, and deep learning to build automated skills at piloting a vehicle while staying in a given lane and avoiding unexpected obstructions, such as pedestrians.
👉 Related Articles:
🎯 Artificial Intelligence: A Complete Overview of Its Pros and Cons
🎯 Top 15 Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools You Need to Know
🎯 Automation Anywhere Interview Questions and Answers
🎯 What is TensorFlow? Learn Here
🎯 Most Frequently Asked Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions in 2025
🎯 AI and Deep Learning Tutorial: Everything you need to know
🎯 Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions and Answers Update:2025
🎯 AI Engineer Salaries in 2025











