
Introduction to Project Design Life cycle
A project life cycle is that the sequence of phases that a project goes through from its initiation to its closure. The number and sequence of the cycle are determined by the management and different alternative factors like requirements of the organization concerned within the project, the character of the project, and its area of application. The phases have an exact begin, end, and management purpose and are constrained by time.
The project lifecycle may be defined and changed as per the wants and aspects of the organization. Even though each project encompasses a definite start and end, the actual objectives, deliverables, and activities vary widely. The lifecycle provides the fundamental foundation of the actions that should be performed within the project, irrespective of the precise work involved.
Basic Things you will Study in this Tutorial:
Characteristics of the Project Life Cycle
Benefits
Options for obtaining a methodology•Life Cycle Project Management

Characteristics of the Project Life Cycle
Although projects are unique and extremely unpredictable, their standard framework consists of same generic lifecycle structure, consisting of following phases:
- The Initiation Phase: beginning of the project
- The Planning Phase: Organizing and preparing
- The Execution Phase: Carrying up the project
- The Termination Phase: Closing the project
The Initiation Phase: The initiation part aims to outline and authorize the project. The project manager takes the given data and creates a Project Charter. The Project Charter authorizes the project and documents the initial necessities for the project. It includes information such as:
Project’s purpose, vision, and mission
Measurable objectives and success criteria
Elaborated project description, conditions, and risks
Name and authority of the project sponsor
concerned stakeholders
The Planning Phase: the aim of this part is to lay down an in depth strategy of however the project should be performed and the way to form it successful.
Project designing consists of 2 parts:
- Strategic planning
- Implementation planning
In strategic planning, the general approach to the project is developed. In implementation planning, the ways in which to use those decisions are sought.
The Execution Phase: During this section, the choices and activities outlined during the planning phase are Implemented. During this section, the project manager needs to supervise the project and prevent any errors from going down. This method is additionally termed as monitoring and controlling. After getting satisfaction from the client, sponsor, and stakeholder’s end, he takes the method to next step.
The Termination Phase: this can be the last part of any project, and it marks the official closure of the project.
This general lifecycle structure is employed with higher management or less number of people accustomed to the project. Some individuals may confuse it with the project management method teams, however then it contains activities specific to the project. The project lifecycle, on the other hand, is freelance of the life cycle of the actual outcome of the project. However, it’s useful to require the present life-cycle part of the product into consideration. It will give a typical frame of reference for comparison totally different comes.
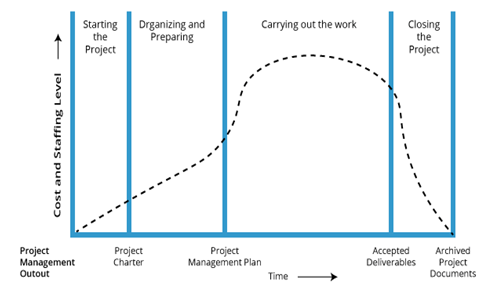
The generic life cycle structure normally exhibits the subsequent characteristics:
•At the beginning, price and staffing levels square measure low and reach a peak once the work is ongoing. It once more starts to drop rapidly because the project begins to halt.
The typical price and staffing curve doesn’t apply to all projects. considerable expenses are required to secure essential resources early in it’s life cycle.
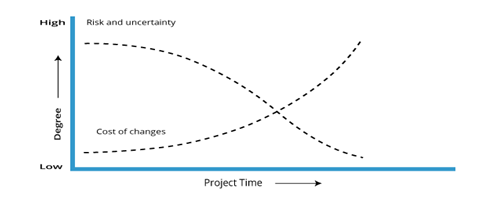
Risk and uncertainty are at their peak at the start of the project. These factors drop over the lifecycle of the project as their choices reached, and deliverables are accepted.
The ability to have an effect on the ultimate product of the project while not impacting the price drastically is highest at the beginning of the project and reduces because the project advances towards completion. It is clear from the figure 2 that the cost of making new changes and rectifying errors will increase as the project approaches completion.
Benefits :
These features are present almost in all kinds of project lifecycles but in various ways. Adaptive life cycles are developed significantly with the intent of keeping stakeholder influences higher and therefore the prices of changes lower through the life cycle than in prognostic life cycles.
Let’s take a glance at how information on project lifecycle advantages for an organization:
It helps professional services teams to be more proficient and profitable.
It helps the organization.
It makes the flow of communication easier.
It emphasizes on reporting and examining previous projects.
Project life cycles will vary from prognostic or plan-driven approaches to adaptive or change-driven approaches. In a prognostic life cycle, the specifics are outlined at the beginning of the project, and any alterations to scope are carefully addressed. In an adaptive life cycle, the product is developed over multiple iterations, and detailed scope is outlined for iteration only as the iteration begins.
Options for obtaining a methodology
To success implement a lifecycle methodology, initial convince yourself that there is worth if the method is applied and used properly. In fact, all comes use a strategy of processes, procedures and templates. If you do not assume you’ve got one, it extremely means you’ve got a poor and informal one.
If you need a good lifecycle methodology, there are 2 major sources.
•Build one yourself. you can build a custom methodology that completely reflects the philosophy and best practices of your organization. several corporations still try this these days.
•Buy one. If you build a strategy, you would possibly be to find out that it ultimately appearance kind of like most alternative lifecycle methodologies that individuals use. in spite of however you structure it, you continue to ought to do some level of study, design, construct, take a look at and implement. Therefore, several corporations selected an choice to obtain or license a pre-existing methodology. These pre-built methodologies typically have everything your organization must achieve success.

Life Cycle Project Management (LCPM)
•Financial metrics such as internal rate of return and cost/worth ratio.
•Customer satisfaction objectives such as functionality, aesthetics, operability, end-user satisfaction, etc.
•Due diligence objectives such as the project’s adherence to regulations and exposure to risks & liabilities
This creates a more integrated approach to project management. While you’ll still break the project into its five stages, you’ll constantly analyze it in terms of its financial, customers, and due diligence objectives.











